| disease | Anal Atresia |
| alias | Anal Atresia, Low Anorectal Atresia, Anal Closure |
Anal atresia, also known as low anorectal atresia, occurs due to abnormal development of the primitive anus, resulting in the failure to form an anal canal and causing the rectum to be disconnected from the outside. In Chinese medicine, it is referred to as "anal closure."
bubble_chart Etiology
Imperforate anus is a type of mid-level malformation commonly seen in clinical practice. Due to developmental disorders of the primitive anus, it fails to invaginate and form the anal canal. The development of the rectum is generally normal, with its blind end located near the edge of the bulbospongiosus muscle of the urethra or the lower end of the vagina, and the puborectalis muscle surrounds the distal end of the rectum. The perineum is often underdeveloped, appearing flat, and the anal region is covered with intact skin. It may be associated with fistulas in the bulb of the urethra, the lower segment of the vagina, or the vestibule.
bubble_chart Clinical Manifestations
After birth, the infant did not pass meconium and quickly developed symptoms of intestinal obstruction such as vomiting, abdominal distension, and fullness. Upon local examination, the perineal center appeared flat, with the anal area partially covered by skin. In some cases, there was a small, pigmented dimple with radiating wrinkles, and stimulation of this area elicited a contraction response of the sphincter muscle. When the infant cried or strained, a bulge appeared in the center of the perineum, and placing a finger in this area could feel an impulse. When the infant was placed in a head-down position with the buttocks elevated, percussion over the anal region produced a tympanic sound.
bubble_chart DiagnosisAfter birth, there is no passage of meconium, and the anal area is covered by skin. There is a sense of impact in the anal area when crying. On an inverted lateral X-ray, the distal end of the rectum is located at or slightly below the pubococcygeal line. Ultrasound and puncture methods indicate that the rectal blind end is approximately 1.5 cm from the anal skin.
bubble_chart Treatment Measures
Surgery should be performed as soon as possible after diagnosis, generally by perineal anoplasty, or alternatively by sacroperineal anoplasty.
Perineal Anoplasty (Figure 1):
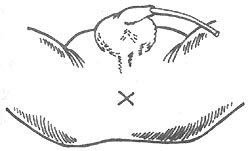
⑴ Incision
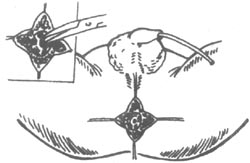
⑵ Separation through the middle of the sphincter
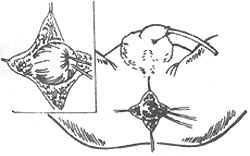
⑶ Freeing the rectal blind end
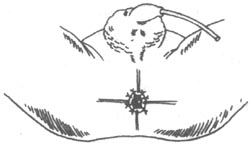
⑷ Anoplasty
Figure 1 Perineal Anoplasty
- Incision: Make an X-shaped incision about 1.5 cm long in the center of the perineum or in the middle of the area that can trigger a circular contraction. Cut through the skin and flip open four skin flaps, beneath which the circular external sphincter fibers can be seen.
- Finding and freeing the rectal blind end: Use ant-like vascular forceps to bluntly separate the soft tissues through the middle of the sphincter towards the deeper layers, where the blue rectal blind end can be found. Pass two thick silk threads through the muscle layer of the blind end for traction. Since the rectal blind end is located within the puborectal muscle ring, it should be separated upwards closely along the intestinal wall. Free the blind end for about 3 cm, allowing the rectum to be pulled loosely to the anal opening. The rectum must be sufficiently freed; if not adequately freed and forcibly pulled down for suturing, postoperative retraction of the intestinal wall is highly likely, leading to cicatricial stenosis. During separation, care should also be taken to avoid injury to the urethra, vagina, and rectal wall.
- Incision of the rectum: Make a cross-shaped incision at the rectal blind end, use a suction device to remove all meconium, or let it flow out naturally and wipe clean. Protect the wound surface as much as possible to avoid contamination. If contamination occurs, rinse carefully with saline.
- Anastomosis and fixation: Fix the rectal blind end to the surrounding soft tissues with several stitches, and use fine silk or catgut to intermittently suture the intestinal wall to the perianal skin with 8-12 stitches. Ensure that the intestinal wall and skin flaps are cross-matched so that the healed scar is not on the same plane. Start anal dilation about 10 days postoperatively to prevent stricture of the anus.





