| disease | Deep Palmar Space Infection |
Acute infection of two adjacent potential spaces in the deep palm caused by deep penetrating wounds or spread from suppurative tenosynovitis.
bubble_chart Etiology
Infection of the midpalmar space is mostly caused by the spread of tenosynovitis in the middle and ring fingers, while infection of the thenar space is due to infection of the tendon sheath of the index finger. It can also occur from direct puncture wounds. The causative bacteria are mostly Staphylococcus aureus.
bubble_chart Clinical Manifestations
(1) Midpalmar space infection The normal concavity of the palm disappears, replaced by swelling, tense and pale skin, with obvious tenderness. The middle, ring, and little fingers are held in a semi-flexed position, and passive extension causes severe pain. Severe edema is present on the dorsum of the hand. Systemic symptoms such as high fever, headache, rapid pulse, and increased white blood cell count may occur.
(2) Thenar space infection Significant swelling and tenderness are observed in the thenar eminence and the thumb web space, but the palm concavity remains. The thumb is slightly abducted and flexed, the index finger is semi-flexed, and movement is restricted, especially the inability to oppose the thumb. Systemic symptoms are present.
1. Acute infection of the midpalmar space Local characteristics are: ① The palmar concavity disappears or becomes slightly raised, with pale skin and obvious pain and tenderness. ② The ulnar three fingers are semi-flexed, and passive extension of the fingers exacerbates the pain. ③ The skin on the dorsum of the hand is red and significantly swollen, often easily mistaken for cellulitis.
2. Acute infection of the thenar space Local characteristics are: ① Significant swelling and tenderness at the first web space and thenar eminence. ② The thumb is abducted, with limited opposition and adduction movements. ③ The index finger is semi-flexed, and passive extension exacerbates the pain. ④ The palmar concavity remains, and swelling on the dorsum of the hand is mild.bubble_chart Treatment Measures
(1) For thenar space infection: Treatment can involve high-dose antibiotics. Local early management is the same as for suppurative felon. If there is no improvement within a short period, early incision and drainage should be performed. A longitudinal incision is made between the middle and ring fingers at the web space, ensuring the incision does not extend beyond the distal palmar crease to avoid injuring the superficial palmar arch of the
stirred pulse. Using hemostatic forceps to spread the subcutaneous tissue allows access to the thenar space (Figure 1). Alternatively, a small transverse incision can be made at the distal palmar crease opposite the ring finger to enter the thenar space. (2) For midpalmar space infection: General treatment is the same as for thenar space infection. The drainage incision can be made directly at the most swollen and fluctuant area of the thenar eminence. Alternatively, an incision can be made at the web space between the thumb and index finger (the "purlicue") or a longitudinal incision can be made on the radial side of the second metacarpal on the dorsum of the hand (Figure 1).
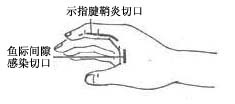
(1) Incision for suppurative tenosynovitis of the index finger and thenar space infection
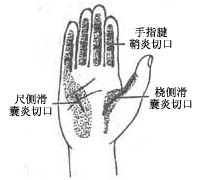
(2) Incision for suppurative tenosynovitis of the finger, ulnar bursitis, and radial bursitis
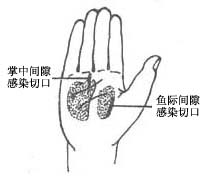
(3) Incision for midpalmar space infection and thenar space infection
Figure 1 Surgical incisions for flexor tenosynovitis, bursitis, and deep palmar space infections of the hand.





