| title | Patchouli |
|---|
| source | Yukezhai |
|---|
Today, patchouli is used as the labiatae plant patchouli Pogostemon cablin (Blanco) Benth. of dry aboveground parts. Patchouli is mainly cultivated. The commercial medicinal materials are divided into Shipaixiang, also known as Paixiang and Zhengxiang, mainly produced in Shipai, Guangdong; Gaoyaoxiang, also known as Zhaoxiang and Zhixiang, mainly produced in Gaoyao County, Zhaoqing City; Zhanxiang is mainly produced in Zhanjiang, Suixi and Xuwen; Nanxiang is mainly produced in Hainan. Among them, Shipai incense has the best quality. In addition to Guangdong and Hainan, it is also cultivated in Guangxi, Fujian, Taiwan, Sichuan, Yunnan, and Guizhou.
materia medica According to research, patchouli Pogostemon cablin of the Lamiaceae family is native to Southeast Asia and was imported as a spice around the Han and Wei dynasties. It is the authentic source of "Cablin Patchouli Herb". This plant has been cultivated on a large scale in Lingnan since the Song Dynasty. late stage [third stage] began to gradually pass off Cablin Patchouli Herb as Cablin Patchouli Herb, a widely distributed wild Lamiaceae plant soil Cablin Patchouli Herb Agastache rugosa, and Pogostemon cablin was forced to change its name to "patchouli" to show the difference. From the perspective of cultivation history, Guangdong has always been the authentic production area of patchouli. 【Variety Review】The large-scale import of plant spices in ancient times is probably related to the Buddhist habit of using incense as offerings. Among all kinds of incense, Cablin Patchouli Herb is also a commonly used product. For example, in Volume 5 of "The Sutra of Guangju Dharani on the Top of the Great Buddha", twelve kinds of incense are used for burning incense. The first one is Cablin Patchouli Herb, whose Sanskrit name is Patchouli incense. On the eighth day of April, when bathing the Buddha, the water was stained with three kinds of herbal incense, namely Duliang incense, Cablin Patchouli Herb, and Aina incense. This is recorded in Volume 33 of Fayuan Zhulin. In addition, "Douluo Po Incense", "Tama Luo Pa Incense" and "Kasuan Incense" in various scriptures are all considered to be Cablin Patchouli Herb. Because Cablin Patchouli Herb is mainly from foreign countries, there are many errors in the records of its plant characteristics in early literature. Typical statements are such as the notes of Yu Yiqi and Han Kangbo in the Eastern Jin Dynasty: "Foreign master Hu said that all the fragrances are one big tree, and the wood flowers are chickens. The tongue, the wood glue is fumigation, the knots are green wood, the roots are sandalwood, the leaves are Cablin Patchouli Herb, and the heart is Chinese Eaglewood Wood.”
This misunderstanding was gradually corrected with the increase of exchanges. According to the books cited in the Huaxiang chapter of Volume 36 of "Fayuan Zhulin", "Guangzhi" said: "Cablin Patchouli Herb comes from the southern countries." Wu. At that time, foreign legends said: "Dukun was in Funan, and Cablin Patchouli Herb came out." "Nanzhou Foreign Objects Chronicle": "Cablin Patchouli Herb came out of Dianxun, a seaside country, belonging to Funan. The fragrance is shaped like Duliang, and can be worn in clothes." Volume 982 of "Taiping Yulan" quoted "Southern Vegetation and Trees" as saying: "Cablin Patchouli Herb is grown by the people. It is harvested in May and June and exposed to the environment. It is fragrant. It is produced in Jiaozhi, Wuping, Xinggu, and Jiuzhou." "The quote from "Jiaozhou Ji" says: "Cablin Patchouli Herb is like Su He." (According to Volume 81 of "Yi Wen Lei Ju", it is quoted as "Cablin Patchouli Herb is like Su." Li Shi-zhen said: "Liu Xinqi's "Jiaozhou Ji" said If Cablin Patchouli Herb is similar to Storax, it means that its spirit is similar, not its shape.") In addition, Du You Tongdian also said: "Cablin Patchouli Herb came out of the Dunxun Kingdom, and it will grow from cuttings." From the above records. Judging from the above, Jiaozhou is located close to Vietnam, Dianxun is also known as Dunxun, and Dukun is a military commander, both in today's Malay Peninsula. From this, it can be seen that the Cablin Patchouli Herb used in ancient times was first introduced from Vietnam, Philippines, Malaysia and other countries .In the early days, Cablin Patchouli Herb was mainly used as spice fumigation or as fragrant powder for external use. Zhouzhou Fang Volume 6 has a hermit effect in treating armpit odor. It says: "slender dutchman's pipe root, Cablin Patchouli Herb, chicken tongue" Two liang each of incense and lead-powder, the four flavors on the right are powdered, and wrapped in cotton under the inner armpits, often as a spread." In the same volume, the six-flavored coriander fragrant side says: "One piece of Chinese Eaglewood Wood, one liang of musk, Storax honey coating , Simmer over low heat, less color will change, beautiful steetgum resin one or two. Pound Chinese Eaglewood Wood until it is broken into soybean grains, clove one or two, do not pound, make three or two sections. Pound until the fragrance remains, mix with honey into a stick, burn If it is a tassel, wear half a tael. It is better to add a tael of Cablin Patchouli Herb." This is what "Nanzhou Foreign Objects Chronicles" said "with clothes on." Mingyi Bielu compiled by Tao Hong-jing was probably confused by Yu Yiqi's theory that all five spices belong to the same tree, so he added Cablin Patchouli Herb to the top-grade Chinese Eaglewood Wood article. Its efficacy is only "curing cholera heart pain". ", Xinxiu Bencao Therefore, "Jiayou materia medica" of the Song Dynasty was first published, and added the effect: "Cure wind edema swelling and poison, remove malign qi." But it is still in the xylem, to Ming Bencao Pinhui Jingyao moved to the lower grade of grass.
The large-scale cultivation of Cablin Patchouli Herb in China should have started in the Song Dynasty. Bencao Tujing said: "Cablin Patchouli Herb used to have five-spice sticks attached to it. It was not found in the state. It is found in many Lingnan counties today. It is also commonly planted. Seedlings germinate in February, with dense stems and clumps. The leaves are like mulberry but small and thin. When picked in June and July, they are fragrant when dried and must turn yellow before harvesting. "According to Zhenglei Bencao painted the Mongolian Cablin Patchouli Herb (Figure 1). Its variety is currently used as Pogostemon cablin.
Cablin Patchouli Herb. Its leaves were used exclusively for medicinal purposes in ancient times. Bencao Gangmu said: "Cablin Patchouli Herb has square stems with weak joints and leaves slightly resembling eggplant leaves. Jiegu and Dongyuan only use its leaves and do not use them. "Twigs and stems, today people use them together with branches and stems, because the leaves are many and false." Today, I checked Taiping Huimin Heji Jufang, "Applicable Prescriptions for Communication", etc., and sure enough, there are many books on "Cablin Patchouli Herb Leaves" , and asked to "remove the sand, soil, branches and stems". Also Bencao Mengquan mentioned: "In Lingnan counties and prefectures, people grow a lot of crops. They harvest them in July, and the smell is very fragrant. Marketers often mix it with cotton leaves and eggplant leaves to pass off, so you have to choose carefully." Pick up the branches and stems and use them as medicine to treat the spleen and lung meridians." Later generations of Cablin Patchouli Herb changed to use the above-ground parts of the plant as a medicine in order to eliminate counterfeiting.
At that time, not only were the leaves of other plants passed off as Cablin Patchouli Herb, but other aromatic plants were also used in various places to collectively call it "Cablin Patchouli Herb". Diannan Bencao had "Cablin Patchouli Herb", which was used to treat stomach heat. , ulcerative gingivitis in children, the organizer identified the original plant as Cablin Patchouli Herb Agastache rugosa (Fisch. et Mey.) O. Kuntze. This plant was used as Cablin Patchouli in the late stage [third stage] of the Ming Dynasty. The name of Herb, "materia medica 成亚halfgatha" says: "Cablin Patchouli Herb came from Jiaozhi, Jiuzhen, Wuping, and Xinggu countries, and the officials and people were diverse. Today, Lingnan is quite fertile, and there are also places there. In February, the root is again It can also be sown by seeds. The seedlings are like Duliang, with square stems clustered in clusters, with empty middle and outer nodes. The leaves are like persimmons with serrated edges. In July, the ears are raised, and the flowers are like polygonum, the houses are like false persimmons, and the seeds are like weeds. Pick the stems and leaves and expose them to dry in May and June when the ears are not in the ear." Bencao Huiyan Same as above. According to the domestically cultivated Pogostemon cablin, it is extremely difficult to flower and bear fruit, and is mainly propagated through cuttings. The Cablin Patchouli Herb described by Lu Zhi-yi, Ni Zhu-mo, etc. has leaves similar to cultivated purple perilla leaf, and the Cablin Patchouli Herb with flowers and ears, In fact, it is Agastache rugosa, but at that time, the name "Cablin Patchouli Herb" was no longer used, and it was called "Cablin Patchouli Herb".
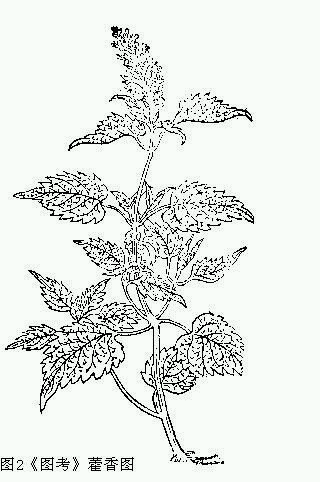
Agastache rugosa may have been the mainstream medicinal Cablin Patchouli Herb in the Qing Dynasty. Not only did most of the materia medica follow the description in "materia medica 成亚halfgatha", Zhiwu Mingshi Tukao Volume 25 also said: " Cablin Patchouli Herb is found in "Southern Herbs" and was first recorded in "Jiayou materia medica". People in Jiangxi and Hunan now use it as a variety. It is a good medicine for repelling summer heat, because it can cure spleen and stomach vomiting, and it must be used to treat cholera." According to the report. The attached picture, (Fig. 2) is also Agastache rugosa. Since Agastache rugosa took over the name Cablin Patchouli Herb in the Qing Dynasty, the Pogostemon cablin produced in Guangdong was forced to change its name to "patchouli" to show the difference.

【Evolution of Authentic】
As mentioned above, patchouli was introduced to China from Southeast Asian countries during the Han and Wei dynasties. At first, only its leaves were used. It was once misrepresented as the leaves of a tree, and there were even records of five spices sharing the same tree. Later, due to the successful introduction, more and more knowledge was gained about this plant. As for the time when Cablin Patchouli Herb was introduced to Han Dynasty, Mr. Xie Zongwan's "Discussion on Chinese Materia Medica Varieties" stated that "Guangzhi" of the Liang Dynasty mentioned that "it is abundant in Lingnan", and therefore believed that "at least before the Liang Dynasty, patchouli was already available in our country." "Introduced and cultivated", we have checked various books citing "Guangzhi", and they all say that "Cablin Patchouli Herb came from the countries in the south of Japan", not Yunnan, and the materia medica in the Tang Dynasty still misunderstood that Cablin Patchouli Herb was woody, then It is clear that it was not widely cultivated at that time, so the introduction time in Lingnan should begin in the Song Dynasty according to the "Illustrated Book". There is also a picture of Cablin Patchouli Herb in Mengzhou in "Zheng Lei". Mengzhou is now Mengshan County, Guangxi. In the Song Dynasty, Cablin Patchouli Herb was cultivated outside Guangdong and even in Guangxi.
The output of patchouli can be seen from the records of Chen Renshan and Cao Bingzhang in the Republic of China. "Drug Production Identification" says: "Cablin Patchouli Herb is produced in Guangdong, preferably Panyu, Henan Baogang, Nanzhuang, and Shipai. Zhaoqing , The sixth step is Zhaoxiang, followed by Qiongzhou, which is produced in Nanxiang." "Updated Weiyao Tiaobian says: "Cablin Patchouli Herb, materia medica named Doulou Poxiang, is the most popular produced in Lingnan. In Baogang Village, Henan Province and Zhaoqing, within a hundred miles of Yangcheng City, new ones appear in May and June, with square stems and pekoe green leaves. The fragrance when rubbed is strong and lingers around the nose. The one with a pungent taste is called patchouli. , buying and selling, Juchang and Taichang are the most authentic places. For example, those produced in Leizhou, Qiongzhou and other places are named Hainan Cablin Patchouli Herb, which is now the so-called foreign Cablin Patchouli Herb. Its qi is thin and turbid, and its taste is spicy and strong. , the leaves are thin and small, the stem is rounded, the stem is long, and the root is the heaviest. Others such as Cablin Patchouli Herb, which is produced in Jiangsu and Zhejiang, can be sliced fresh, dried in the hot sun, and stored in a vat, so that the aroma cannot be stored. It is also very effective as medicine, no less effective than patchouli."