| title | Giant Knotweed |
| release time | 2005/12/30 |
| source | Jade Knock Studio |
The dried rhizome and root of Giant Knotweed, Polygonum cuspidatum Sieb. et Zucc., from the Polygonaceae family, is currently used. It is mainly produced in Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Anhui, Guangdong, Guangxi, Sichuan, Yunnan, Henan, Guizhou, and other regions, predominantly wild, with some cultivated varieties.
Materia medica research suggests that since the "Erya," the Polygonaceae plant Giant Knotweed has been a mainstream medicinal herb. This product is widely distributed, with no distinct regional specificity. However, ancient materia medica records indicate medicinal production in Zhejiang, Anhui, Sichuan, Henan, Yunnan, and other provinces.
bubble_chart Varietal Examination
The "Erya" states: "Tu, Giant Knotweed." Guo Pu annotates: "Resembles princes-feather herb but is coarser and larger, with fine thorns, can be used to dye red." The "Mingyi Bielu" names the root of Giant Knotweed, and Tao Hongjing says, "It is very common in the fields, resembling large Polygonum, with spotted stems and round leaves." According to the "Bielu," princes-feather herb is also mentioned, described as "resembling Polygonum but larger, growing by water," its original plant being Polygonum orientale L. of the Polygonaceae family, while large Polygonum refers to Polygonum lapathifolium L. of the same genus. From the descriptions by Guo and Tao, Giant Knotweed should be the same as Polygonum cuspidatum of the Polygonaceae family.
The "Shu Bencao" Tujing states: "Grows in wet lowlands, forming trees over a zhang tall, with red stems and yellow roots, found everywhere." Su Song's "Bencao Tujing" provides a more precise description: "Sprouts in March, stems like bamboo shoots, with red spots, branches upon sprouting, leaves like small apricot leaves, flowers in July, fruits in September. Those from the south do not flower, roots with black skin, yellow inside when broken, resembling willow roots. Some are over a zhang tall." According to the attached "Yuezhou Giant Knotweed" medicinal illustration (Figure 1), its rhizome is thick, stems have spots, nodes have stipule sheaths, undoubtedly the modern Giant Knotweed.
However, a careful analysis of the texts and illustrations from previous materia medica cited in the "Zhenglei Bencao," besides the "Yuezhou Giant Knotweed," the illustrated "Chuzhou Giant Knotweed" should also be a Polygonaceae plant, but the "Fenzhou Giant Knotweed" clearly is not. Moreover, the attached text from the "Bencao Yanyi" about Giant Knotweed is also peculiar. Kou Zongshi first negates the "Shu Bencao" Tujing's claim, then states: "Giant Knotweed generally resembles cold chrysanthemum, but with larger flowers, leaves, stems, and pistils, still with pale black spots on stems and leaves, blooming from June to July, until mid-September, flowers with four petals, color like peach blossoms, slightly larger, slightly darker outside, very common in Shaanxi mountain foothills and water edges." According to Kou's description, it closely resembles the "Fenzhou Giant Knotweed," its original plant unknown, while the Polygonaceae Giant Knotweed is unisexual, dioecious, forming dense axillary panicles, with slender pedicels, joints in the middle, wings above, very small flowers, perianth deeply 5-lobed, white or pale green-white, clearly not the same plant.Despite the confusion in Giant Knotweed varieties during the Song dynasty, since the Ming and Qing dynasties, the Polygonaceae Giant Knotweed has been correctly used. Besides Giant Knotweed, some other plants in ancient materia medica may be related to this product, involving changes in production areas, briefly discussed below.
- Ceratostigma root is mentioned in the *Bencao Tujing*, classified under the category of external herbs. The text states: "Ceratostigma root grows in the suburbs of Yizhou. It tastes bitter and has a cold nature. It is primarily used to relieve wind congestion, excessive heat, restlessness, thirst, and mania. The leaves are collected in spring and summer, ground, soaked in cold water, and the juice is extracted and consumed, which is highly effective. Its stems and leaves resemble those of Mentha. It is also known as '斑骨草' (Bangu Cao) or '斑杖絲' (Banzhang Si)." Some researchers believe that the properties and functions of ceratostigma root are similar to those of Giant Knotweed (*Polygonum cuspidatum*). In *Shaanxi Chinese Herbal Medicine*, Giant Knotweed is also referred to as "搬倒甑" (Bandaozeng). Additionally, the medicinal illustration of ceratostigma root in the *Tujing* depicts alternate, elliptical leaves and spotted stems, resembling the seedlings of Giant Knotweed. Therefore, it is suggested that ceratostigma root may be the seedling of Giant Knotweed. (See Sun Jian: "A Study on Ceratostigma Root in *Bencao Tujing*," *Shizhen Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Medica*, 1999; 10(9): IX.) However, there are differing opinions. The *Xinhua Materia Medica Compendium* suggests that the ceratostigma root in the *Tujing* is *Patrinia villosa* Juss. from the Patrinia family, while Ye Guorong argues that it is *Eupatorium japonicum* Thunb. from the Asteraceae family. (See Ye Guorong et al.: "A Materia Medica Study on Ceratostigma Root," *Chinese Medicinal Materials*, 2002; 25(3): 200-201.) In reality, the description and illustration of ceratostigma root in the *Tujing* are brief, and the arguments presented by various scholars are insufficient. The true identity of ceratostigma root remains a subject for further research.
- Suan Tong Sun is mentioned in Jiuhuang Bencao: "It grows by the mountain streams of Shaohua Mountain in Mi County. Initially, it sprouts with bamboo shoot leaves, then branches out with stems, reaching a height of four to five feet. The stems resemble those of the water knotweed but are red in color. Its leaves are similar to those of the white hibiscus but are rough, and also resemble the leaves of the mountain thistle, which are also rough with coarse veins. The taste is sweet with a slight sourness." Since the plants recorded in "Jiuhuang" are all based on the author's personal observations and the illustrations are accurate (Figure 2), it is undoubtedly the Polygonaceae plant Giant Knotweed (Polygonum cuspidatum).
 圖1、Yuezhou Giant Knotweed
圖1、Yuezhou Giant Knotweed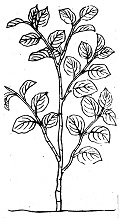 圖2、"Relief for Famine" Giant Knotweed
圖2、"Relief for Famine" Giant Knotweed - Diannan Bencao mentions Ban Zhuang Gen, and "Tukao" Volume 20 cites it under the third illustration of Air Potato. Combining the discussion on the names and realities of Air Potato in Bencao Gangmu, Wu Qi-jun stated: "What Li Shi-zhen called Huang Yao is today's Suan Gan, known as Ban Zhuang Gen in Yunnan." The current compilers of Diannan Bencao correctly identified this as Giant Knotweed.
- Bencao Gangmu Volume 18, under the category of vine herbs, lists Air Potato, whose authentic species should be the Dioscoreaceae plant Dioscorea bulbifera L. However, the entry for Air Potato in Gangmu states: "Nowadays, it is cultivated everywhere. Its stems are two to three feet tall, soft and jointed, resembling vines but not actually vines. The leaves are as large as fists, about three inches long, and do not resemble mulberry leaves. The roots are about a foot long, with the larger ones two to three inches in circumference, brown outside and yellow inside, sometimes reddish-yellow. The flesh color is similar to Japanese dock root, and people often pound the roots to add to dye vats, saying it changes color easily." This is actually the third illustration of Air Potato in Zhiwu Mingshi Tukao Volume 20, which is the Polygonaceae Giant Knotweed. It seems Li Shi-zhen did not truly recognize Giant Knotweed. In Volume 16, under the category of wetland herbs, Li first explained its name: "The staff refers to its stem, the tiger to its spots," which is correct. However, his description of the Giant Knotweed plant states: "Its stem resembles that of the knotweed, its leaves are round like apricots, its branches yellow like willows, its flowers resemble chrysanthemums, and its color is like peach blossoms." This is clearly a patchwork of quotes from Guo Pu, Su Song, and Kou Zong-shi. As for the "flowers resembling chrysanthemums, color like peach blossoms," and the medicinal illustration of Giant Knotweed in Gangmu being based on the "Fenzhou Giant Knotweed" from "Tujing," these all expose Li Shi-zhen's ignorance. It is no wonder he mistakenly identified Giant Knotweed as Air Potato, rightly criticized by Wu Qi-jun.
- Caomu Bianfang mentions Suan Tang Geng, with a rhyme stating: "Suan Tang Geng sour, dispels wind poison, treats yin sores with Chinese wax myrtle bark for application and washing. Removes malignant toxins, decay, hemorrhoids, and fistulas, and eliminates wind-dampness, cinnabar heat." Tianbao Materia Medica mentions Suan Tong, with a rhyme stating: "Suan Tong, also known as Realgar Lian, treats dampness-heat of spleen and stomach, and grub qi. It can relieve pain in the muscles and bones throughout the body, and cure hand and foot cramps." The compilers of both books correctly identified these as the Polygonaceae Giant Knotweed.
bubble_chart Historical Evolution of Authentic Production Areas
Giant Knotweed is widely distributed in Hebei, Henan, Shandong, Jiangsu, Anhui, Zhejiang, Jiangxi, Fujian, Taiwan, Hubei, Hunan, Guangdong, Guangxi, Sichuan, Guizhou, Yunnan, Tibet, and other provinces and autonomous regions, with no distinct authentic production area. However, ancient materia medica records clear medicinal production areas such as Zhejiang (based on the "Yuezhou Giant Knotweed" illustration in "Tujing"), Anhui (based on the "Chuzhou Giant Knotweed" illustration in "Tujing"), Sichuan (based on Shu Bencao, Caomu Bianfang, and Tianbao Materia Medica), Henan (based on Jiuhuang Bencao), and Yunnan (based on Diannan Bencao). These can serve as the basis for establishing GAP bases for this product.
bubble_chart Other Related Items




